Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
When planning a project that requires a durable, transparent, or translucent material, you’ve likely come across polycarbonate sheets. Touted as a superior alternative to glass and acrylic, this versatile plastic has revolutionized industries from home improvement to large-scale commercial construction. But what exactly are polycarbonate panels, and are they the right choice for your specific needs? This in-depth guide will walk you through their properties, types, benefits, and common applications to help you make an informed decision.
What Are Polycarbonate Sheets?
At its core, polycarbonate is a incredibly strong thermoplastic polymer. Think of it as a material engineered for resilience. Unlike glass, which is hard but brittle, polycarbonate is virtually unbreakable, offering a unique combination of strength and flexibility. Its molecular structure allows it to absorb significant impact without cracking or shattering, a property that makes it the material of choice for safety and security applications.
The most common form you’ll encounter is multi-wall polycarbonate sheets. These panels are engineered with multiple layers (often two to four walls, but sometimes more) separated by vertical ribs. This structure creates air pockets that provide exceptional thermal insulation, making them ideal for roofing and glazing.
Types of Polycarbonate Panels
Understanding the different types available is key to selecting the right product for your project.
-
Solid Polycarbonate Sheet: These are single, thick, and flat panels, much like a piece of glass but far stronger. They are excellent for applications requiring maximum impact resistance and clarity, such as protective barriers, machine guards, and security glazing.
-
Multi-Wall Polycarbonate: As mentioned, this is the go-to choice for insulated roofing and siding. The multiple walls trap air, providing excellent heat retention in winter and heat reflection in summer. They are lightweight, easy to install, and diffused light beautifully, reducing harsh shadows. Common profiles include dual-wall, triple-wall, and even five-wall for extreme insulation needs.
-
Corrugated Polycarbonate: These sheets feature a classic wavy pattern. They are primarily used for roofing on sheds, patios, carports, and agricultural buildings like greenhouses. The corrugated design adds structural strength and allows for easy overlapping during installation, ensuring a watertight seal.
-
Textured or Embossed Polycarbonate: These sheets have a pattern on one or both sides that diffuses light and provides privacy. They are perfect for interior applications like room dividers, shower enclosures, or decorative panels where you want to let light in but obscure the view.
Key Benefits and Advantages
Why choose polycarbonate over other materials? The advantages are numerous:
-
Unmatched Impact Resistance: This is its standout feature. Polycarbonate sheets are over 200 times stronger than glass of the same thickness and about 30 times stronger than acrylic. They can withstand hail, thrown objects, and even attempted break-ins, making them a premier choice for impact-resistant roofing and security windows.
-
Lightweight and Easy to Install: Polycarbonate panels are about half the weight of glass and significantly lighter than acrylic. This makes them much easier to handle, cut, and install, reducing both labor time and the need for heavy supporting structures.
-
Excellent Thermal Insulation: The multi-wall polycarbonate design provides a high R-value (a measure of insulating power), which can lead to substantial energy savings by reducing heating and cooling costs. This makes them a smart, long-term investment for any structure.
-
High Light Transmission: These sheets allow abundant natural light to filter through, creating bright, inviting spaces while diffusing the light to eliminate harsh glares and hot spots. This quality of natural daylighting is beneficial for both homes and commercial buildings.
-
UV Protection: Virtually all quality polycarbonate sheets come with a co-extruded UV-resistant layer on one side. This coating blocks harmful UV rays, protecting whatever is underneath from fading, while also ensuring the panel itself does not yellow or become brittle from sun exposure over many years.
-
Safety and Security: In the unlikely event of breakage, polycarbonate cracks into large, blunt pieces without sharp shards, much like a car windshield. This makes it a much safer option in environments with children or in areas prone to severe weather.
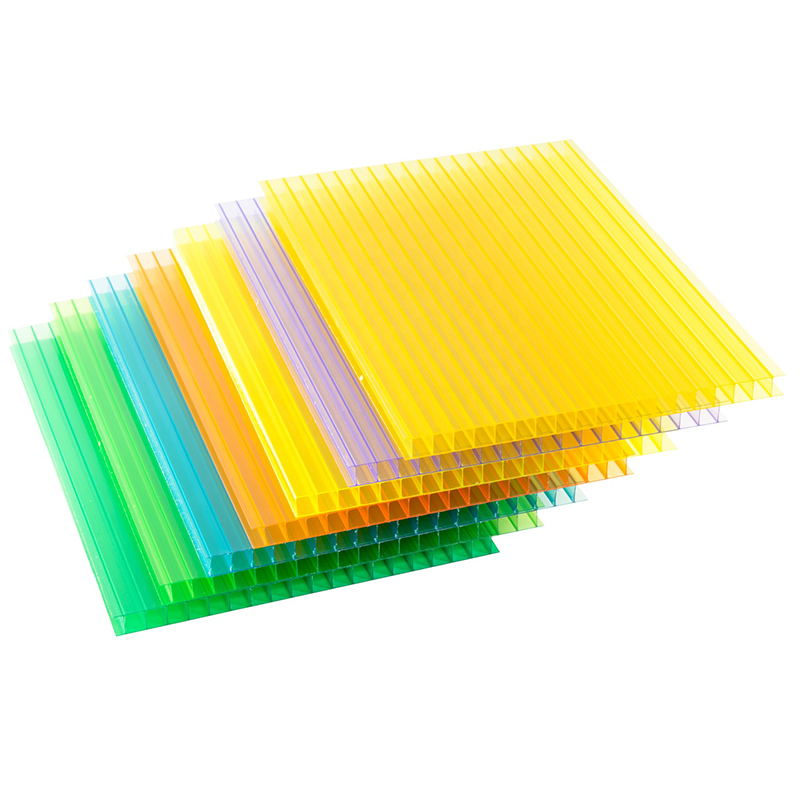

Common Applications and Uses
The properties of polycarbonate sheets make them suitable for a vast range of projects:
- Roofing and Glazing: The most popular use. Patio covers, pergola roofs, skylights, sunrooms, and greenhouse panels all benefit from its strength, insulation, and light-diffusing properties.
- Greenhouses: Provides a perfect microclimate for plants by retaining heat, diffusing sunlight to prevent leaf burn, and protecting against hail and high winds.
- Noise Barriers: Used along highways and in industrial areas because certain multi-wall structures also provide effective sound dampening.
- Protective Barriers: From hockey rinks and bus shelters to factory machine guards and security windows in stores.
- DIY and Interior Design: Used for shed windows, garage door panels, light covers, and modern interior design elements like sliding doors and partitions.
Installation Tips and Considerations
A successful installation ensures longevity and performance.
- Handle with Care: While tough, the surface can be scratched. Handle sheets by the edges and leave the protective film on during installation, removing it only after the job is complete.
- Correct Orientation: Always install polycarbonate sheets with the UV-protected side facing outwards, toward the sun. This is usually marked on the protective film.
- Allow for Expansion: Plastic expands and contracts with temperature changes. When installing, use appropriate fasteners (like self-tapping screws with thermal washers) and drill oversized holes to allow the sheet to move slightly without stress.
- Seal Properly: Use the correct sealing tapes: non-porous tape for the top edges to keep out water and dust, and porous tape for the bottom edges to allow for condensation drainage and ventilation.
Conclusion
Polycarbonate sheets offer a powerful combination of durability, insulation, and light transmission that is difficult to match with any other single material. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to build a durable patio cover, a gardener designing a resilient greenhouse, or a business owner needing secure glazing, understanding the properties and types of polycarbonate panels is the first step. By weighing its significant benefits against your project’s specific requirements, you can confidently choose a solution that will provide clarity, protection, and efficiency for years to come.